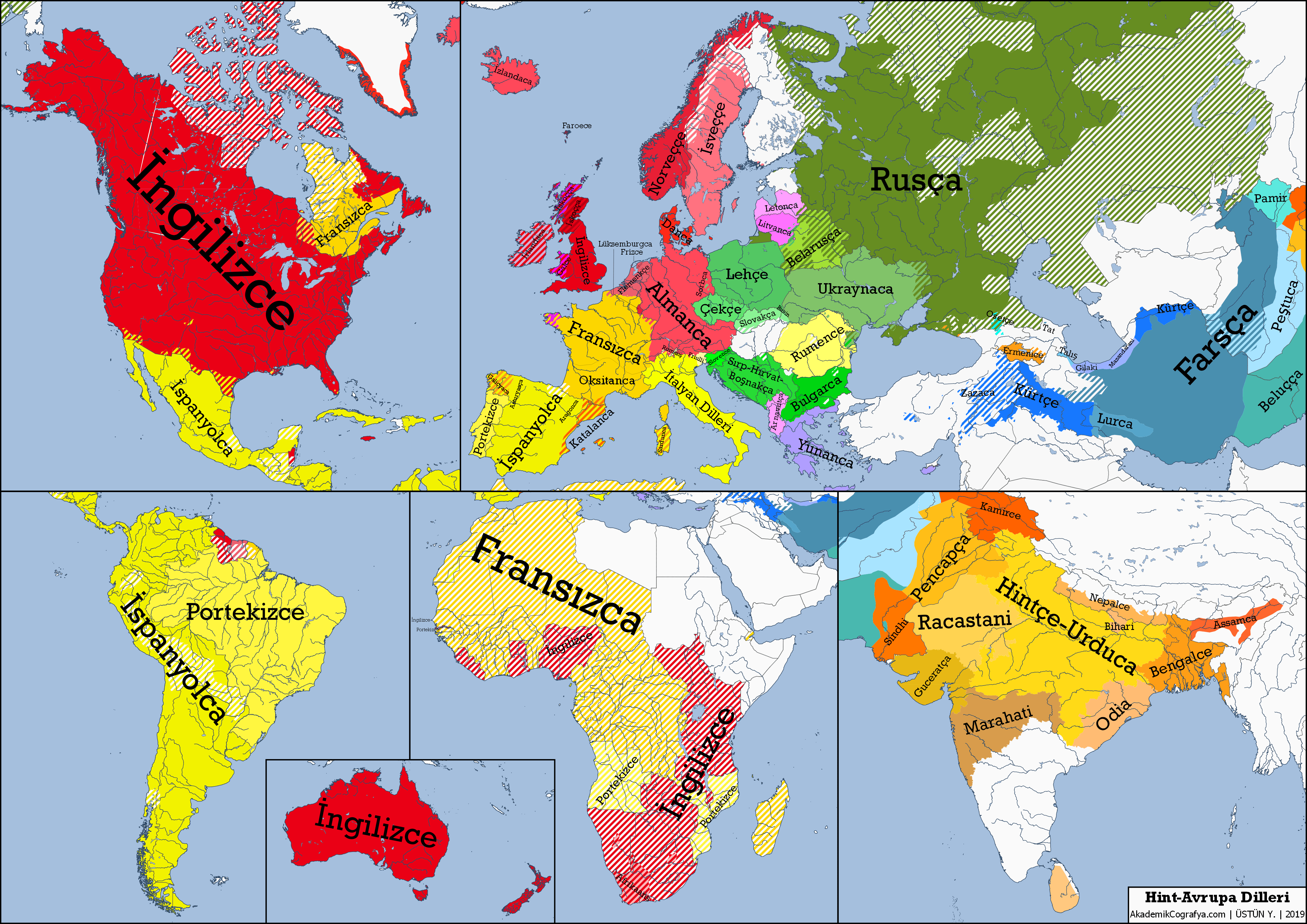
The Indo-European languages form a vast family that encompasses over 400 distinct languages spoken by nearly 40% of the world’s population today. Recent genetic research reveals fascinating insights into their ancestry, tracing the origins back about 6,500 years to a group of people known as the Caucasus Lower Volga inhabitants. These early speakers were pivotal in shaping the linguistic landscape we recognize now, having intermingled with diverse groups across the region, influenced by the notable Yamnaya culture. This groundbreaking discovery not only sheds light on the origin of Indo-European languages but also connects linguistic evidence to genetic data, providing a clearer picture of how languages evolve over time. By delving into the history and migration patterns of these ancient peoples, we can better understand the intricate tapestry of language development that has played a crucial role in human civilization.
The languages of the Indo-European family represent a significant linguistic lineage, tracing back to ancient cultures that once thrived across the Eurasian steppes. Through meticulous research, scholars have linked modern languages, such as Latin, Greek, and Sanskrit, to their early speakers who roamed the fertile lands of the Lower Volga region. These innovative communities, often referred to as the ancestors of Indo-European languages, laid the groundwork for linguistic interactions that spanned continents, shaped cultures, and influenced societies. As genetic studies uncover the complex interplay of migration and cultural diffusion, the evolution of these languages becomes a remarkable narrative of human adaptation and change through time. Understanding the roots of such a widespread linguistic family not only enriches our appreciation of language itself but also highlights the shared history of diverse cultures.
Exploring the Ancestry of Indo-European Languages
The Indo-European language family is not just a cornerstone of linguistic studies, but it also threads a narrative of human history that spans millennia. The recent scientific investigations reveal that the origins of these languages lie deeply rooted in the past, particularly amongst the Caucasus Lower Volga individuals who inhabited modern-day Russia around 6,500 years ago. This finding not only provides a tangible ancestry to the diverse languages spoken today but also bridges the gap between linguistics and genetics, allowing a holistic understanding of how these languages evolved and spread across continents.
Research highlighted by geneticists like David Reich has emphasized that the Yamnaya culture, linked to these ancient communities, played a pivotal role in disseminating the proto-Indo-European language. The hypotheses formed around these early speakers have built a framework to analyze the linguistic similarities found across Indo-European languages. It illustrates the profound interaction between languages and cultures, especially during a time when economic and social transformations were occurring in Europe and beyond.
The Yamnaya Culture and Its Influence
The Yamnaya culture represents a significant chapter in the story of Indo-European languages, showcasing how the movement of pastoral communities facilitated linguistic exchange and evolution. This culture, characterized by their nomadic lifestyle and use of wheeled vehicles, has been substantiated through historical and archaeological records. Their innovations in herding and mobility allowed them to traverse vast distances, integrating their language with existing local dialects and cultural practices. Through this lens, we can see how the Yamnaya served not just as speakers of an ancestor language but also as cultural conduits, enabling the spread of Indo-European languages across Europe and parts of Asia.
Moreover, genetic research has laid out a more nuanced pathway of the Yamnaya’s influence on modern European populations. As they migrated and mixed with indigenous groups, significant demographic changes ensued, resulting in a unique blend of genetics that mirrored the linguistic shifts occurring at the time. The Yamnaya’s legacy is therefore imprinted not solely in the words spoken today but also in the very DNA that connects contemporary populations across different regions.
Genetic Research on the Origins of Indo-European Languages
The integration of genetic research with linguistic studies represents a groundbreaking advancement in our understanding of Indo-European languages. By examining ancient DNA from archaeological sites, researchers have traced lineage connections that elucidate the migration patterns of early Indo-European speakers, particularly focusing on the Caucasus Lower Volga people and their interaction with the Yamnaya culture. This interdisciplinary approach not only affirms long-held theories regarding the Eurasian Steppe as a language-birthplace but also adds a vital layer to our comprehension of population dynamics during the Eneolithic period.
In 2015, significant insights came to light, demonstrating how the Yamnaya were instrumental in altering the genetic landscape of Europe through extensive migration and genetic mixing. The data illuminates historical population structures, providing evidence that significant portions of modern European ancestry can be traced back to these ancient groups. As such, the genetic studies not only bolster the steppe hypothesis but also offer a robust framework for future research on the relationships between language, culture, and genetic heritage.
Caucasus Lower Volga: The Cradle of Indo-European Languages
The Caucasus Lower Volga region is increasingly recognized as the cradle of Indo-European languages, housing the earliest speakers who shaped the linguistic landscape of today. This area, rich in cultural and historical significance, provides essential context for understanding how early languages evolve and spread. The research tracing the ancestry of these speakers showcases their role as a foundational group in linguistics, marking them as pivotal in the timeline of human communication.
Exploring the languages that stemmed from this region reveals a complex interplay between environment, culture, and communication. By studying linguistic similarities and DNA evidence, scholars are piecing together a remarkable picture of the ancestral roots from which modern European and Asian languages have sprung. This convergence of linguistics and genetic studies has illuminated how the Caucasus Lower Volga people not only contributed to language development but also transmitted cultural practices that resonated throughout history.
The Role of Culture in the Spread of Indo-European Languages
Culture is an undeniable force in the propagation of languages, and the Yamnaya culture exemplifies this phenomenon. As mobile pastoralists, the Yamnaya were not just transporting livestock; they were also carriers of their language, customs, and traditions. This blend of economic innovation and social practices allowed for a dynamic exchange of ideas and language among various groups they encountered, presenting a model of how cultural attributes can influence linguistic development and diffusion.
Moreover, the burial practices of the Yamnaya, which involved constructing kurgans, demonstrate their cultural significance in shaping sociolinguistic identity. Such traditions not only provided a physical means of preserving the memory of their ancestors but also reinforced social structures that cohesively tied language and identity together. Thus, understanding the cultural context of these early speakers illuminates how the Indo-European languages continued to evolve even as they spread across diverse populations.
Linguistic Similarities Among Indo-European Languages
The linguistic similarities across the Indo-European language family have fascinated scholars for centuries. From Latin to Greek, to Sanskrit and its progeny, researchers have scrutinized the frameworks that unite these languages, revealing the profound connections in vocabulary, grammar, and syntax. This unifying thread points to a common ancestry traced back to the prehistoric speakers of the Indo-European languages, reinforcing theories suggested by genetic evidence of the Caucasus Lower Volga people.
Linguistic studies suggest that the patterns of similarity are not merely coincidences but are reflective of shared cultural and social experiences. Through comparative analysis and the reconstruction of Proto-Indo-European words, scholars are uncovering the foundational elements of these languages, which emerged amidst early migrations initiated by cultures like the Yamnaya. The evolving understanding of these similarities paves the way for further exploration of how languages can transform while remaining interconnected.
Historical Perspectives on Indo-European Language Development
The development of Indo-European languages invites a rich historical perspective that spans archaeological findings and linguistic analysis. The historical narratives constructed by scholars provide a broad understanding of how these languages evolved over time, influenced by migration, interaction, and socio-political factors. The significance of the Caucasus Lower Volga region in this evolution underscores the role of specific communities and cultures in shaping linguistic evolution, emphasizing the interconnectedness of language, culture, and history.
As historical linguists continue to unravel the complex tapestry of Indo-European languages, they draw upon historical documents, archaeological evidence, and genetic studies to piece together a cohesive narrative. This collaborative approach not only clarifies the sequence of geographical and temporal shifts but also illuminates the socio-cultural milieu that facilitated such transformations. Such integrative efforts are paramount as they offer a comprehensive depiction of linguistic evolution influenced by ancient peoples across time.
Impacts of Ancient DNA Studies on Linguistic Research
Ancient DNA studies have revolutionized the field of linguistic research, providing a scientific backbone to hypotheses regarding the origins and spread of Indo-European languages. By establishing genetic links between various populations, researchers can corroborate linguistic similarities with tangible biological evidence. This intersection of genetics and linguistics marks a significant advancement, allowing us to trace language development not just through words but also through the movements and interactions of people across regions.
The implications of these studies extend beyond mere academic curiosity; they challenge traditional narratives surrounding language evolution by presenting a multifaceted view that includes migration and intercultural exchange. As genetic analyses reveal the ancestry of ancient populations, scholars gain insights into how languages influenced and shaped the identities of those who spoke them. This approach invites a more nuanced understanding of how language was disseminated, adapted, and transformed across the tapestry of human history.
Future Directions in the Study of Indo-European Languages
The future of Indo-European language studies is poised for exciting developments as interdisciplinary collaborations continue to flourish. By combining linguistic insights with genetic evidence, researchers are delving deeper into the complexities of language evolution and its relation to human migration patterns. New technologies in sequencing and data analysis will enable scholars to uncover finer details about the demographic shifts that influenced the typography of these ancient languages.
Additionally, as more archaeological findings come to light, there’s potential to refine existing models regarding the spread and breakdown of languages within the Indo-European family. This means not just tracing historical pathways but also understanding the impact of environmental factors, social dynamics, and cultural exchanges in shaping linguistic trajectories. The interplay of these fields will enrich our understanding of how Indo-European languages evolved over time, revealing connections that resonate through the ages.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the origin of Indo-European languages according to recent genetic research?
Recent studies suggest that the origin of Indo-European languages can be traced back to the Caucasus Lower Volga people, who lived in present-day Russia approximately 6,500 years ago. This finding is supported by genetic evidence that indicates these early speakers intermixed with various local populations, forming the linguistic ancestor of over 400 languages spoken today.
How did the Yamnaya culture contribute to the spread of Indo-European languages?
The Yamnaya culture, known for its nomadic pastoralist lifestyle and advanced use of horses and wagons, played a crucial role in disseminating Indo-European languages across Europe and into Asia. Their migration from the steppes north of the Black and Caspian Seas around 5,000 years ago facilitated the spread of their language, which is believed to be a precursor to many modern Indo-European languages.
What role did genetic research play in understanding the ancestry of Indo-European languages?
Genetic research has been pivotal in mapping the lineage of Indo-European languages by analyzing ancient DNA samples from populations like the Yamnaya and Caucasus Lower Volga groups. This research has revealed significant mixing of these groups with other populations, providing a clearer picture of how languages evolved and spread across regions through migration and intermarriage.
What evidence supports the connection between the Caucasus Lower Volga people and Indo-European languages?
Evidence linking the Caucasus Lower Volga people to Indo-European languages includes genetic data that shows a direct line of descent from these early populations to later groups that spoke Indo-European languages. This connection, uncovered through advanced DNA analysis, helps to unify the genetic and linguistic history of these languages.
Why are the Yamnaya considered important in the study of Indo-European languages?
The Yamnaya are considered critical in the study of Indo-European languages because they are believed to be the initial carriers of the proto-Indo-European language into various parts of Europe and Asia. Their cultural and technological advancements, coupled with their extensive migrations, significantly influenced the linguistic landscape of the regions they inhabited.
What impact did the Yamnaya’s burial practices have on our understanding of Indo-European languages?
The burial practices of the Yamnaya, particularly their use of kurgans (large burial mounds), have provided archaeologists with valuable insights into their culture and lifestyle. These sites have yielded genetic material that has been essential for understanding the ancestry of Indo-European languages and how they have evolved over millennia.
Are there any competing theories regarding the origin of Indo-European languages?
Yes, there are competing theories regarding the origin of Indo-European languages, including the Anatolian hypothesis, which suggests that these languages spread from Anatolia (modern-day Turkey) rather than the Eurasian steppe. However, recent genetic findings appear to bolster the steppe hypothesis, which posits that the Caucasus Lower Volga and Yamnaya cultures were central to the languages’ dissemination.
How do modern studies differentiate between the various Indo-European languages?
Modern studies utilize both linguistic reconstruction and genetic analysis to differentiate between various Indo-European languages. By examining the genetic makeup of ancient populations alongside the phonetic and grammatical features of the languages, researchers can trace their development and establish relationships among different language branches.
What are some examples of Indo-European languages spoken today?
Indo-European languages encompass a diverse array of languages spoken across the globe, including major ones such as English, Spanish, French, Russian, Hindi, and German. These languages have evolved over centuries and are categorized into several branches, including the Germanic, Romance, and Slavic groups.
What did recent research reveal about the cultural practices of Indo-European speakers?
Recent research has unveiled that cultural practices among Indo-European speakers, such as burial customs and pastoralism, were significant in understanding their societal structures and interactions. These practices, highlighted in the context of the Yamnaya culture, reflect how linguistic and cultural elements spread alongside genetic intermixing.
| Key Finding | Details |
|---|---|
| Origin of Indo-European Languages | Identified as the Caucasus Lower Volga people from present-day Russia, approximately 6,500 years ago. |
| Cultural Background | These early speakers lived during the Eneolithic period, intermixing with local populations. |
| Significance of Research | Provides a crucial link in the linguistic history and origin of over 400 Indo-European languages. |
| Previous Theories | Yamnaya people were previously thought to be the originators based on archaeological evidence. |
| Methodology | Research utilized ancient DNA analysis from archaeological sites in Russia and Ukraine. |
| Historical Impact | The research points to significant demographic changes in Europe related to language spread. |
Summary
Indo-European languages represent a pivotal linguistic group that has been traced back to the Caucasus Lower Volga people approximately 6,500 years ago. This groundbreaking research sheds light on the origins and spread of these languages, providing insights into the ancient civilizations that helped form the linguistic landscape of Europe, Asia, and beyond. By examining the genetic evidence and cultural practices of these early populations, scholars have significantly advanced our understanding of the evolution and interconnection of Indo-European languages.